BIOMIMICRY
- OCEAN VIEW -
OUR CHALLENGE TO BIOLOGY
How does nature create conditions for information exchange, resource exchange and abundance?
INNOVATIONS
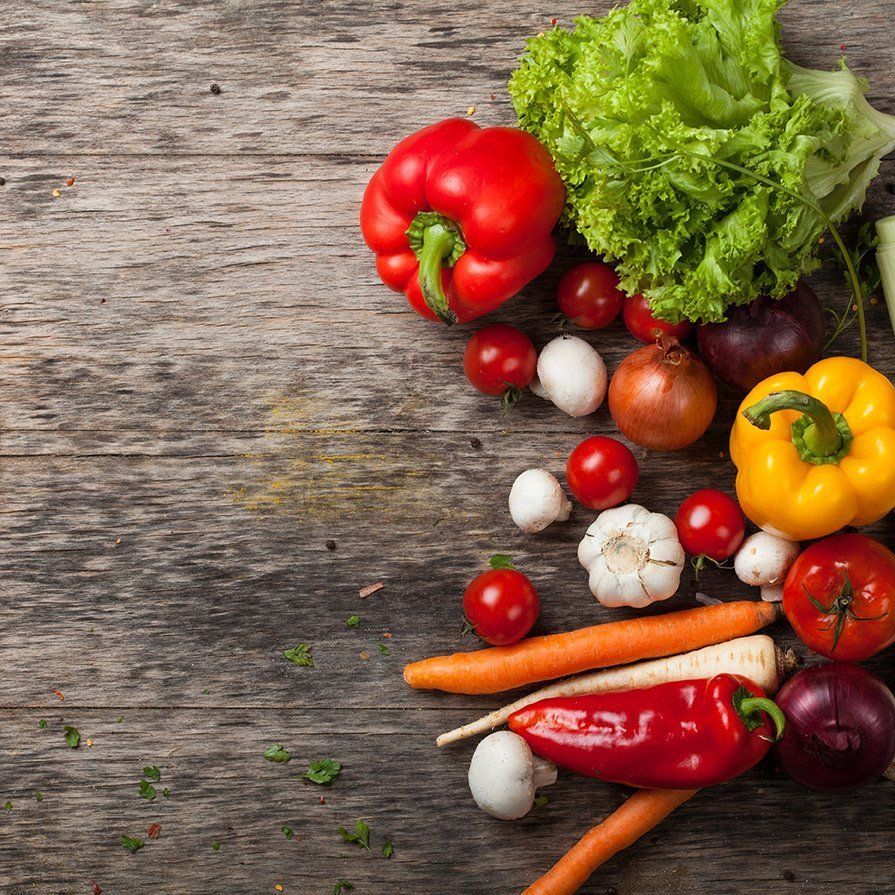
Agri-Produce
Bikers distributing agri-produce to points of sale and homes based on online orders
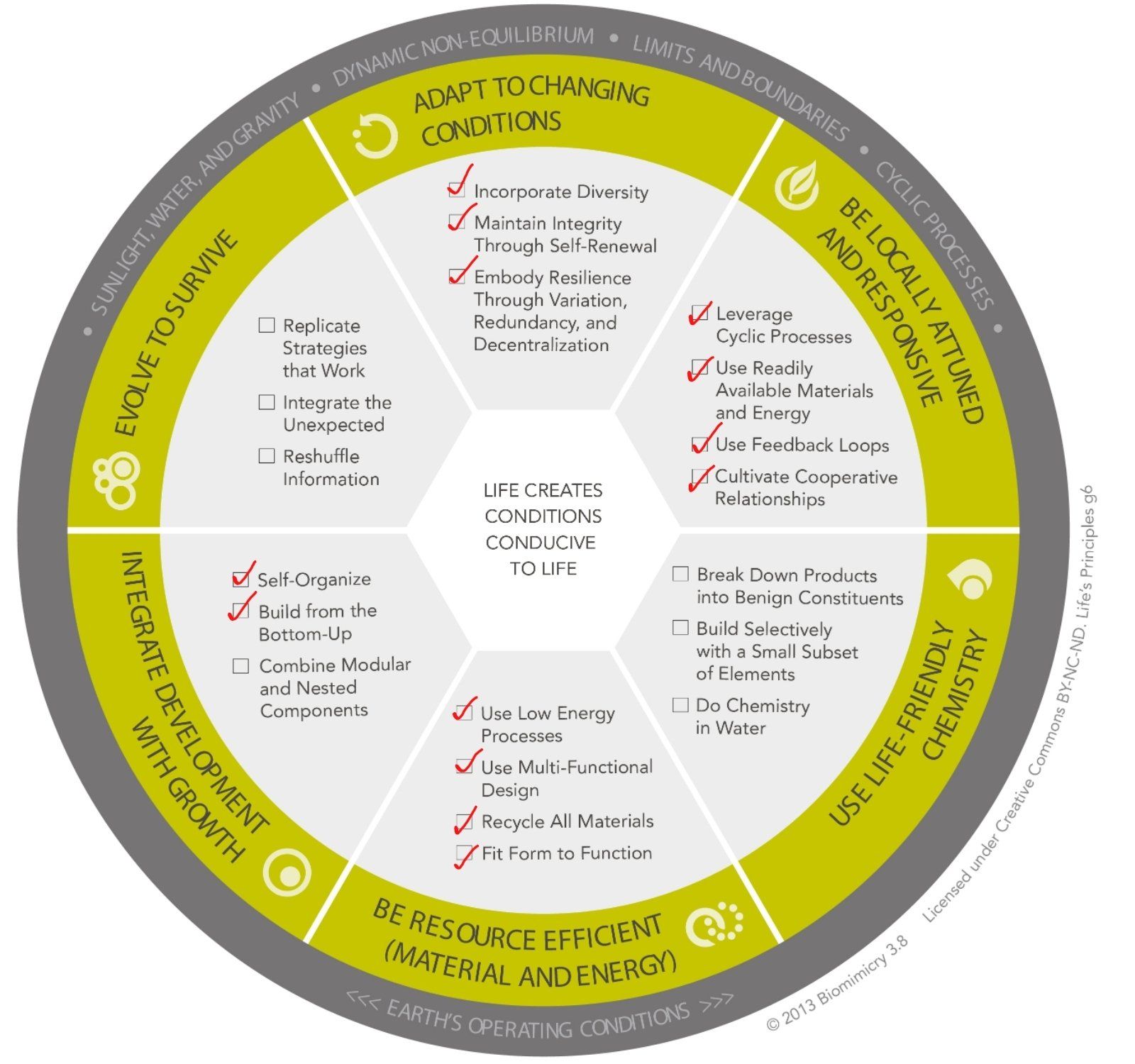
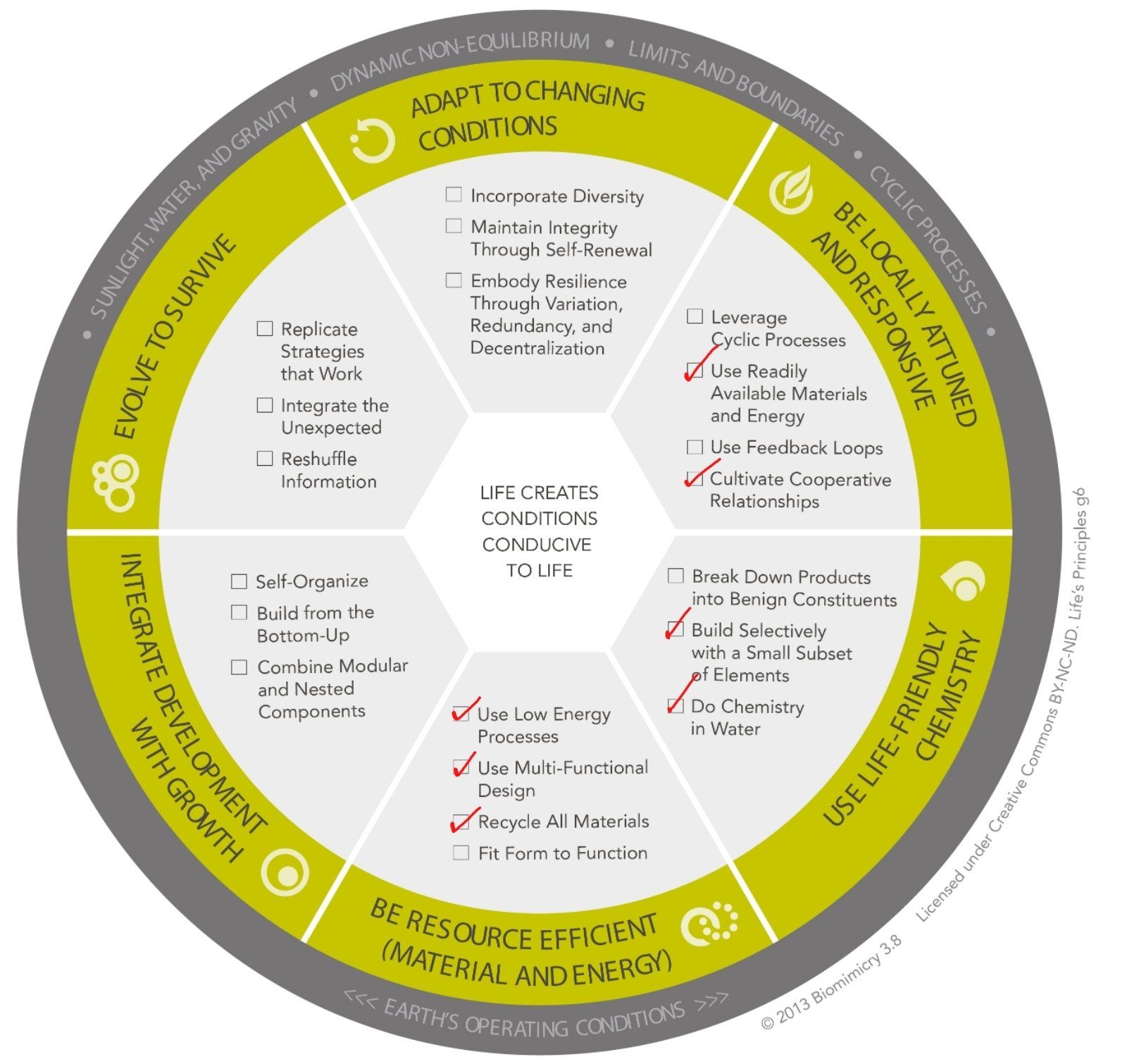
APPLICABLE LIFE'S PRINCIPLES
OUR NEXT CHALLENGE TO BIOLOGY
How does nature harness free energy?
Fish swim in groups so they can protect themselves from predators and to save energy. As fish swim, they shed tiny vortices. When swimming in large schools, the individual fish transfer energy to one another with these vortices, lowering the collective energy costs of swimming. Scientists at Caltech discovered that wind turbines arranged in proximity to interact with their neighbours are more efficient than those operating individually. Furthermore, the wind direction does not matter. Inspired by the way fish can reduce the energetic loss by swimming in a school, vertical axis wind turbines are placed close together so that individual turbines can capture downstream airflow produced by neighbouring turbines. This configuration of the array of turbines reduces the total area needed for the turbines while increasing energy output by up to 10-fold.
INNOVATIONS
WIND ENERGY
Develop vertical axis wind turbines that can harvest wind energy from any direction in a small wind farm.
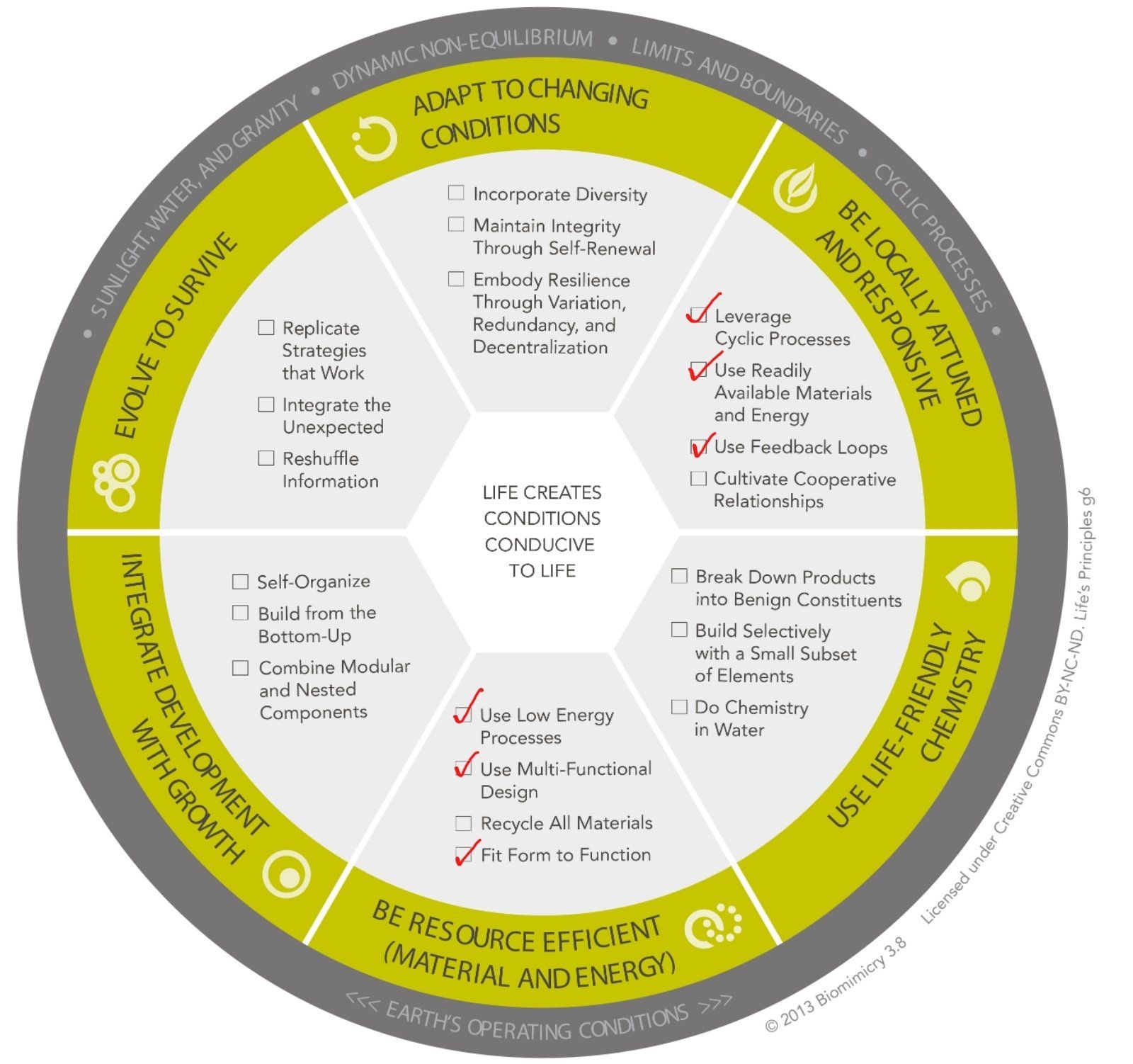
APPLICABLE LIFE'S PRINCIPLES
OUR NEXT CHALLENGE TO BIOLOGY
How does nature manage locally available resources?
INNOVATIONS
Packaging
Kelp as a component in packaging products that need to be wrapped and protected